Are your workout supplements doing more harm than good? Are you wondering whether Workout Supplements can cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Discover the potential link between popular fitness enhancers and erectile dysfunction (also known as impotence).
- Introduction
- What Are Workout Supplements? How Can They Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
- Understanding Erectile Dysfunction
- Common Factors of ED
- The Science Behind the Connection of Workout Supplements to ED
- The Debate: Can Workout Supplements Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
- Recommendations for Workout Supplement Users
- Conclusion
- Final Thoughts and Recommendations
Introduction
In today’s fitness-centric world, workout supplements have become a staple for many gym-goers and athletes. These supplements promise enhanced performance, quicker muscle recovery, and a host of other benefits.
While workout supplements are often marketed for their benefits, it’s crucial to understand their full impact on the body, including sexual health. The purpose of this blog post is to explore a question that has been lingering in the minds of many: Can bodybuilding supplements cause erectile dysfunction?
Given the increasing prevalence of both workout supplement usage and erectile dysfunction cases, it’s a question that warrants serious consideration. We aim to dissect this issue by examining scientific studies, expert opinions, and real-world experiences.
“Many workout supplements contain stimulants that can affect blood pressure and heart rate, which in turn could potentially affect erectile function. Always consult a healthcare provider if you’re on heart medication.”
Dr. Mark Johnson, Cardiologist

However, as the consumption of these supplements rises, so do concerns about their potential side effects. One question that has recently caught the attention of both the fitness community and medical professionals is whether workout supplements can lead to erectile dysfunction (ED).
Erectile dysfunction is a medical condition that affects a significant portion of the male population, particularly as they age. The condition can have various causes, ranging from psychological factors to underlying health issues.
Given the widespread use of workout supplements, examining if there’s a connection between these popular products and the incidence of ED is crucial.
This blog post will delve into the science behind workout supplements and erectile dysfunction, drawing on scholarly research and mainstream articles.
For instance, an academic paper published in PubMed Central (PMC) discusses the adverse effects of long-term use of sports supplements, including their potential link to erectile dysfunction. Another article from Harvard Health provides a nuanced view of the relationship between exercise and ED.
Stay tuned as we unravel this complex issue, backed by scientific evidence and expert opinions.
What Are Workout Supplements? How Can They Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
Workout supplements have become an integral part of the modern fitness landscape. They promise to boost performance, speed up recovery, and help achieve various fitness goals. But what exactly are these supplements, and what types are commonly used?
Definition
Workout supplements are products designed to improve athletic performance and recovery. They come in various forms, including powders, capsules, and liquids, and are often consumed before, during, or after a workout. These supplements contain a range of ingredients, from proteins and amino acids to vitamins and minerals. These ingredients are aimed at enhancing physical performance and reducing fatigue.
Types of Workout Supplements
Types of workout supplements, along with their primary role and common ingredients, are given below:
| Type | Primary Purpose | Common Ingredients |
| Protein Powders | Aid in muscle recovery and growth | Whey, Casein, Plant-based proteins |
| Creatine | Improve strength and power output | Creatine Monohydrate |
| Amino Acids | Muscle recovery, reduce soreness | BCAAs, EAAs |
| Pre-Workouts | Boost energy before workouts | Caffeine, Beta-alanine, Nitric oxide |
| Fat Burners | Aid in fat loss | Caffeine, Green Tea Extract |
| Vitamins and Minerals | Fill nutritional gaps | Multivitamins, Vitamin D, Calcium |
| Testosterone Boosters | Increase testosterone levels | Zinc, Fenugreek, Tribulus |
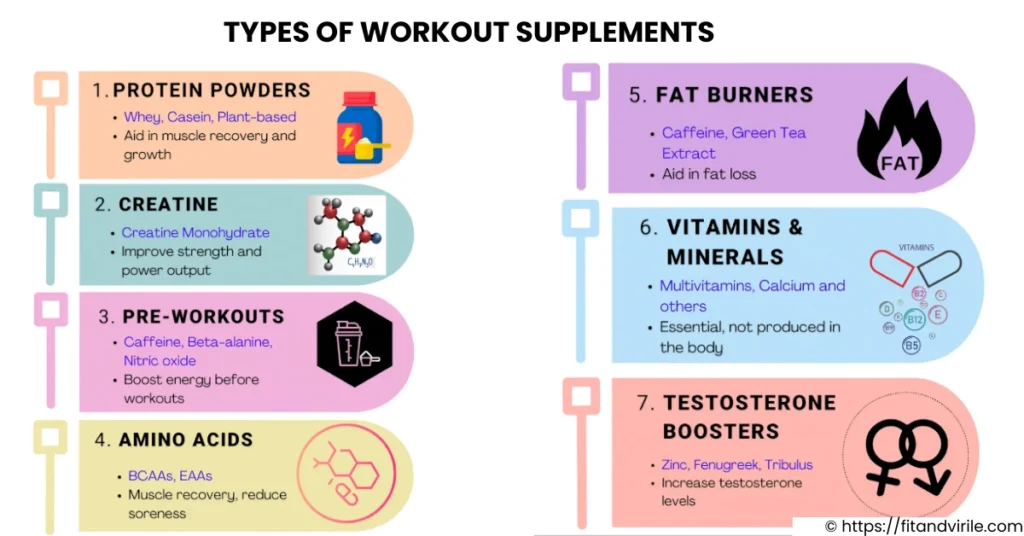
Note: According to a Healthline article, vitamins and minerals, which are commonly used workout supplements, also play a crucial role in sexual health, making it even more critical to understand what you’re consuming.
Why the Concern?
Given the wide variety of workout supplements available, it’s essential to scrutinise their potential side effects, especially concerning sexual health. As mentioned in a PMC study, long-term use of such supplements could potentially lead to adverse effects, including erectile dysfunction.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the scientific evidence that explores the link between these popular workout supplements and erectile dysfunction.
Popular Ingredients Found in Workout Supplements
Let us examine what scientific literature has to say about some of the most popular ingredients found in workout supplements. We have summarised results from the latest scientific publication to answer our question: Can workout supplements cause erectile dysfunction (ED)/impotence?
Whey Protein
- Purpose: Muscle recovery and growth.
- How it Works: Whey protein provides a quick source of amino acids, the building blocks of muscle. It is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream, helping to repair and rebuild muscle tissue damaged during exercise.
- General Concerns: Excessive consumption can lead to kidney issues.
- ED Concerns: No direct link to ED, but excessive protein intake may affect hormone balance.
- Reference: Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health
Creatine Monohydrate
- Purpose: Increases strength and power during high-intensity workouts.
- How it Works: Creatine helps regenerate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of the cell, allowing for increased workout intensity and duration.
- General Concerns: It may cause dehydration and muscle cramps.
- ED Concerns: Some reports suggest it may affect testosterone levels, which could indirectly lead to ED.
- Reference: PMC
Caffeine
- Purpose: Boosts energy and focus.
- How it Works: Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, increasing alertness and reducing the perception of effort and pain.
- General Concerns: Can lead to insomnia, jitters, and increased heart rate.
- ED Concerns: High doses can lead to anxiety and insomnia, which are risk factors for ED.
- Reference: Verywell Health, PMC
Beta-Alanine
- Purpose: Enhances endurance.
- How it Works: Beta-alanine increases the concentration of carnosine in muscles, which helps buffer acid in the muscle, reducing muscle fatigue. Read here for a more detailed explanation.
- General Concerns: This may cause a tingling sensation in the skin.
- ED Concerns: No known direct link to ED.
- Reference: WebMD
BCAAs (Branched-Chain Amino Acids)
- Purpose: Aids in muscle recovery.
- How it Works: BCAAs are metabolised directly in the muscle, helping to accelerate recovery and reduce muscle soreness.
- General Concerns: Overconsumption can lead to fatigue and loss of coordination.
- ED Concerns: Overconsumption can lead to an imbalance in serotonin levels, potentially affecting sexual function.
- Reference: NaoMedical
L-Arginine
- Purpose: Increases blood flow.
- How it Works: L-arginine is converted into nitric oxide in the body, which dilates blood vessels and improves blood flow.
- General Concerns: This may cause gastrointestinal issues.
- ED Concerns: While often used to treat ED, excessive amounts could lead to imbalances.
- Reference: PubMed, SAGE Journals
Green Tea Extract
- Purpose: Promotes fat loss.
- How it Works: Green tea extract contains catechins, which help increase metabolic rate and fat oxidation.
- General Concerns: Excessive consumption can lead to liver damage.
- ED Concerns: Contains caffeine, which in high doses can lead to ED-related issues like anxiety and insomnia.
- Reference: Justea, PMC
Zinc
- Purpose: Supports testosterone production.
- How it Works: Zinc is essential for the enzymatic reactions that produce testosterone, the key hormone for male sexual function.
- General Concerns: High doses can lead to nausea and lowered immunity.
- ED Concerns: Excessive zinc can inhibit the body’s ability to absorb other essential minerals, potentially leading to ED.
- Reference: Healthline, PubMed
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (impotence) is the inability to achieve or maintain a rigid penile erection suitable for satisfactory sexual intercourse.
If you are unable to achieve a satisfactory erection 50% of the time, it may indicate erectile dysfunction. While no specific time period is part of this definition, some experts suggest that the condition needs to persist for at least six months to be considered ED (NCBI).
How an Erection Happens
Understanding the physiological process of an erection can shed light on how various factors, including workout supplements, might influence sexual function. A better understanding of the correction process would benefit us in finding out How Workout Supplements Cause Erectile Dysfunction.
Here’s a breakdown of how an erection occurs:
Understanding the physiological process of an erection can shed light on how various factors, including workout supplements, might influence sexual function. Here’s a breakdown of how an erection occurs:
- Nitric Oxide (NO) plays a crucial role in the erection process. When sexual arousal occurs, the brain sends signals to nerve cells in the penis. These nerve cells release NO, which stimulates an enzyme that produces cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). cGMP is the chemical responsible for relaxing the smooth muscles in the penis, allowing blood to flow more freely (Physiology, Erection – StatPearls – NCBI Bookshelf).
- The penis contains three cylindrical chambers: two corpora cavernosa and one corpus spongiosum. The corpora cavernosa are the primary structures that fill with blood during an erection. When the smooth muscles relax due to the action of cGMP, blood flows into the corpora cavernosa, making the penis rigid and erect. The pressure builds up in these chambers, and the veins that usually drain blood from the penis are compressed, maintaining the erection (Cleveland Clinic, WebMD).
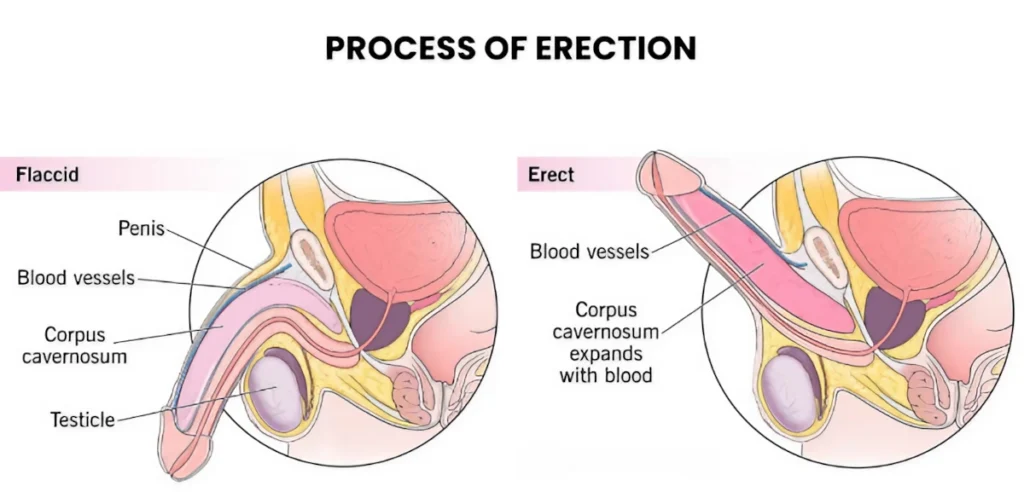
Root Cause of ED
Any cause that disrupts the cascade of physiological events leading to an erection could cause ED, such as:
- The brain’s ability to send signals
- The release of NO
- Vasoconstriction and impaired Blood Flow
- The relaxation of smooth muscles in the corpus cavernosum.
For a detailed explanation of the process of erection and erectile dysfunction, please refer to Cleveland Clinic.
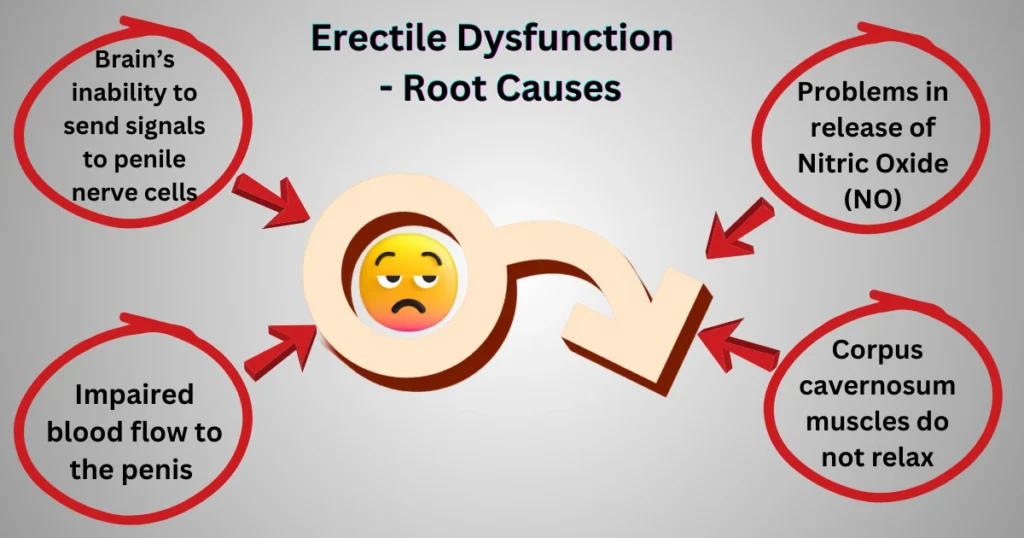
Common Factors of ED
Erectile dysfunction can be caused by a variety of factors (as categorised in the table below). Each of these factors can give rise to ED due to the involvement of one or a combination of the four root causes of ED that disrupt the physiological events leading to erection.
| Category | Common Causes | Disruption in Physiological Events |
| Vascular Conditions | Hypertension, High cholesterol, Atherosclerosis | It affects blood flow, reducing the efficacy of NO and impairing smooth muscle relaxation in the corpus cavernosum. |
| Neurological Conditions | Parkinson’s, Multiple sclerosis, Spinal injuries | It impairs the brain’s ability to send signals, affecting NO release and muscle relaxation. |
| Mental Health Conditions | Stress, Anxiety, Depression | It affects the brain’s ability to send signals, impacting NO release and muscle relaxation. |
| Hormonal Imbalance | Low levels of testosterone | Low testosterone can impair neural signalling and NO release, affecting muscle relaxation. |
| Medications and Treatments | Antidepressants, Antihypertensives | Some medications can inhibit NO release and affect smooth muscle relaxation. |
| Lifestyle Factors | Smoking, Excessive alcohol consumption, Lack of physical activity | Lifestyle factors can affect vascular health, reducing NO efficacy and impairing muscle relaxation. |
Statistics Related to Erectile Dysfunction
Understanding the prevalence and demographics of erectile dysfunction can provide valuable insights into its impact on society. Here are some key statistics:
- Global Prevalence: The worldwide prevalence of erectile dysfunction is expected to increase to 322 million men by 2025 (International Journal of Impotence Research, 2000).
- Prevalence in the United States: About 30 million men in the United States are affected by ED (Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension, 2012).
- Lifetime Risk: It is estimated that 1 in 10 men will experience ED at some point in their lifetime (SingleCare).
- Age Factor: The risk of developing ED increases with age. While ED can affect men in their 20s and 30s, the prevalence is significantly higher among men over 40 (Healthline).
The Science Behind the Connection of Workout Supplements to ED
While there is a lack of direct scholarly evidence linking workout supplements to erectile dysfunction (ED), it’s crucial to explore the potential mechanisms that could theoretically affect erectile function. This section aims to shed light on this understudied area, drawing upon the known effects of common ingredients found in workout supplements.
Vasoconstriction and Blood Flow
Ingredients like caffeine are known for their vasoconstrictive properties, which could theoretically impair blood flow to the penis, affecting the efficacy of nitric oxide (NO) and the relaxation of smooth muscles in the corpus cavernosum.
Hormonal Imbalance
Some workout supplements contain ingredients that can interfere with hormonal balance. For example, excessive zinc intake can decrease the production of other essential hormones, potentially affecting erectile function.
“Hormonal imbalances can affect erectile function. Some workout supplements can interfere with hormone levels, so it’s essential to monitor for any changes.”
Dr. Emily Brown, Endocrinologist
Adulteration Risks
Given the lack of strict regulation in the supplement industry, it’s not entirely out of the realm of possibility for workout supplements to be adulterated with substances like sildenafil, posing potential health risks.
Neurological Effects
Ingredients like caffeine can also affect the central nervous system, potentially interfering with the brain’s ability to send signals for an erection.
Long-term Effects: A Closer Look
The long-term use of certain workout supplements can pose a risk to liver health. Some ingredients commonly found in these supplements have been associated with liver toxicity:
- DMAA (1,3-dimethylamylamine)
- Anabolic Steroids
- Green Tea Extract
- Yohimbe
- Alkylated Testosterone
A prospective study published in the National Library of Medicine found that 8% of Hepatotoxicity Induced by Herbal and Dietary Supplements (HILI) cases from 2010 to 2012 were due to bodybuilding supplements (Source).
Interaction with Medications
Long-term use of supplements could interact with other medications you may be taking, including those for treating hypertension, diabetes, or heart conditions, all of which can affect erectile function (Source).
Insights from Healthline
An article on Healthline primarily discusses the role of vitamins and other supplements like L-arginine and L-carnitine in ED. While these are not exclusively workout supplements, they are sometimes included in workout supplement formulations. The article emphasises that ED is not a standalone condition but a symptom with multiple underlying causes. It also suggests that while some supplements claim to improve ED, the evidence is often anecdotal and not backed by scientific studies (Source).
The Debate: Can Workout Supplements Cause Erectile Dysfunction?
The potential link between workout supplements and erectile dysfunction (ED) is a subject of ongoing debate. While some evidence suggests a possible connection, other studies and opinions argue that the relationship is not so straightforward. In this section, we try ad address our moot question: Can Workout Supplements Cause Erectile Dysfunction? We try to present a balanced view of the conflicting opinions and studies.
The Case For a Connection
Some scholarly articles and health experts raise concerns about the long-term use of workout supplements, citing potential risks such as hormonal imbalances, liver toxicity, and even ED. The lack of regulation in the supplement industry also adds to these concerns.
The Case Against a Connection
On the other hand, proponents of workout supplements argue that when used responsibly and in moderation, these products do not pose a significant risk for ED. They emphasise the lack of direct evidence linking workout supplements to ED and point out that many of the cited risks are theoretical or based on extreme cases of misuse.
The Middle Ground
There is also a middle ground in this debate, suggesting that the risk of developing ED from workout supplements may depend on various factors such as the type of supplement, the duration of use, and individual health conditions.
Outcome
Given the conflicting opinions and lack of conclusive evidence, the safest approach is to exercise caution. If you’re considering using workout supplements and are concerned about ED, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider for personalised advice.
Recommendations for Workout Supplement Users
Given the potential risks associated with workout supplements, it’s essential to approach their use with caution, especially if you’re concerned about erectile dysfunction (ED). This section offers practical recommendations for those who use or are considering using workout supplements.
Practical Recommendations
- Read Labels Carefully
- Always read the labels of workout supplements carefully. Look for third-party testing and certification to ensure the product’s quality and safety.
- Limit Duration of Use
- If you decide to use workout supplements, consider limiting the duration of use and taking regular breaks. This can help mitigate potential long-term effects, including liver toxicity and hormonal imbalances.
- Monitor for Side Effects
- Be vigilant about monitoring for side effects, including signs of ED. If you experience any adverse effects, discontinue use and consult a healthcare provider.
- Exercise Caution with Online Purchases
- Be extra cautious when purchasing supplements online, as the risk of encountering adulterated or counterfeit products is higher.
- Consider Natural Alternatives
- For those concerned about ED, consider natural alternatives to improve physical performance and erectile function. These could include dietary changes, regular exercise, and stress management techniques.
When to Consult a Healthcare Provider
It’s advisable to consult a healthcare provider in the following situations:
- Before Starting New Supplements:
- Always consult a healthcare provider before starting a new supplement regimen, especially if you already take other medications.
- Experiencing Side Effects:
- Seek medical advice immediately if you notice any adverse effects, including signs of ED, hormonal imbalances, or liver issues.
- Long-Term Use:
- If you’ve been using workout supplements for an extended period, having regular check-ups to monitor for any potential long-term effects is a good idea.
- Pre-existing Medical Conditions:
- If you have pre-existing medical conditions like hypertension, diabetes, or heart disease, a healthcare provider can offer personalised advice on the safety of workout supplements.
- Lack of Improvement:
- If you’re using workout supplements to improve athletic performance or other aspects of physical health and don’t see any improvement, consult a healthcare provider for alternative solutions.
“While there’s no conclusive evidence linking workout supplements to ED, caution is advised. Always consult a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement, especially if you have pre-existing conditions.”
Dr. John Smith, Urologist
Conclusion
Finally, we return to our question: Can Workout Supplements Cause Erectile Dysfunction? The answer is No and Yes. The potential link between workout supplements and erectile dysfunction (ED) is a complex and debated subject.
While some studies suggest that certain ingredients in workout supplements may pose risks, the evidence is inconclusive. The lack of regulation in the supplement industry further complicates matters. Given these uncertainties, exercising caution and consulting healthcare providers for personalised advice is crucial.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
- Be Informed
- The first step in making safe choices is to be well-informed. Always do your own research and consult healthcare providers for personalised advice.
- Exercise Caution
- Given the ongoing debate and potential risks, it’s essential to approach workout supplements cautiously. Opt for products that have been third-party tested and read labels carefully.
- Consult a Healthcare Provider
- If you’re considering using workout supplements and have concerns about ED or other health issues, a healthcare provider can offer a thorough evaluation and personalised advice.
- Consider Natural Alternatives
- Natural alternatives like a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques can often provide the same benefits as workout supplements without the potential risks.
- Monitor Your Health
- Be vigilant about monitoring for any side effects, including signs of ED. If you experience any adverse effects, seek medical advice immediately.
By following these recommendations, you can make more informed decisions about using workout supplements while minimising potential risks, including ED.
Nowadays a new type of supplement MK-677 has gained attention as a “miracle drug” among bodybuilders for its potential benefits, ranging from muscle growth to fat loss and even possibly boosting testosterone levels. It’s also gaining traction in the field of men’s sexual health. Read more here.
Explore the connection between erectile dysfunction (ED) and pre-workout supplements by reading here.
NOTE: This article doesn’t intend to serve as medical advice. Please read our disclaimer.

